- HAProxy is free, open source software written in C that provides a high availability layer 4 and layer 7 load balancing and proxying. It has a reputation for being fast and efficient (in terms of processor and memory usage).
- HaProxy configuration II. Global Defaults global log 127.0.0.1 local0 maxconn 4096 chroot /usr/share/haproxy user haproxy group haproxy daemon option redispatch maxconn 2000 contimeout 5000 clitimeout 50000 srvtimeout 50000.
Download Prometheus, the leading open-source monitoring framework and TSDB. This includes support for PromQL, the powerful Prometheus query language for processing your monitoring data in a flexible. Alternatives to Haproxy for Linux, Windows, Mac, Web, Self-Hosted and more. Filter by license to discover only free or Open Source alternatives. This list contains a total of 14 apps similar to Haproxy. List updated: 8:56:00 PM.
In general when you are load balancing a cluster you can evenly spread the connections through the cluster and you get pretty consistent and even load balancing. However with some applications such as RDS (Microsoft Terminal Servers), you might get very high load from just a few users doing heavy work. This in turn could result in slow performance for other users on the same server.
The solution to this problem is to use some kind of server load feedback agent.
The Loadbalancer.org appliance has had an adaptive feedback agent for a while now. However with a LOT of help from Simon Horman (of UltraMonkey fame) - we've managed to integrate the functionality into the main branch of HAproxy.
We also thought it would be a good idea to open source our previous work on Ldirectord/LVS, make it compatible with HAProxy, and release our Windows service code as GPL.
UPDATE: The Loadbalancer.org feedback agent code is now fully supported in HAProxy 1.5-dev21 + and all future versions. Alcatech bpm studio pro.
UPDATE 31/10/2018: Complete rewrite in a language called GO..
Our Windows feedback agent has recently undergone a complete rewrite in a language called GO. We felt that our previous implementation of the feedback agent was feeling a bit dated, requiring an older version of the .net framework and was becoming a pain to maintain. With this new version, the agent technically allows for cross-platform compatibility, improves performance as GO is a compiled language, and lastly is so much easier to support. A more detailed explanation of the benefits and setbacks of getting thus far will be explained in a future blog.
It is also worth mentioning that with this release we added a new feature that allows for you to specify the port in the feedback agent config.
Our GO feedback agent is open source and can be found on Github here.
The previous agent is still available on Github here.
How do I install the feedback agent on Windows?
Please remove any previous version of the feedback agent before installing version 4.5.4 and above as it is a completely new installer. Furthermore, you will need to install .net framework.
Simply download the latest Windows Feedback Agent installation package here:
http://downloads.loadbalancer.org/agent/loadbalanceragent.msi (v4.5.6) [Updated 08/02/2019]
The feedback agent functionality is available in all versions of the Loadbalancer.org appliance software for both layer 4 (Ldirectord) and layer 7 (HAProxy).
Assuming that you have downloaded and installed the msi file from the link above, you should be able to find the simple client here:C:ProgramDataLoadBalancer.orgLoadBalancermonitor.exe
Simply hit the 'start' button and the agent should start responding to telnet on port 3333 (you may need to make an exception for that port in your Windows firewall).
Then make sure you modify your virtual server on the load balancer to poll the feedback agent:
Then on the Windows server client:
You can change the 'mode' setting to drain then 'apply settings and restart' and HAProxy will then set the weight to 0 and status to drain (blue) i.e.:
Or you can set the 'mode' to halt then 'apply settings and restart' and HAProxy will then immediately set the status to DOWN (yellow) i.e.:
When the agent is running in normal mode it will report back the percentage idle of the system based on the settings in the feedback agent XML file:
C:ProgramDataLoadBalancer.orgLoadBalancerconfig.xml
Notice that you can control both the importance of CPU & RAM utilization and also a threshold, so the following logic is used:

- If CPU importance = 0 then ignore, 0.5 means give 50% importance, 1 means 100% importance
- If RAM importance = 0 then ignore etc.
If ThresholdValue is reached on any monitor then immediately go into DRAIN mode (a value of 0 means no threshold is set).
This can be very useful if you have a small number of RDP sessions using a lot of RAM, simply set a ThresholdValue of 85, then as soon as memory crosses that threshold no new users will be sent to that server.
Otherwise to calculate the percentage idle reported by the agent would be to divide the utilization by the number of factors involved i.e.
If you are using two services then:
- utilization = utilization + cpuLoad * cpuImportance%;
- utilization = utilization + ramOccupied * ramImportance%;
- utilization = utilization / 2
So if importance was 1 for both cpu and ram you would only get 0% reported if both CPU and RAM were 100%. (actually it gets a bit weird if one is already reporting 0%, but lets not worry about that..
And if the importance is zero then ignore completely i.e.
- AS: utilization = utilization + cpuLoad * cpuImportance%;
- IF: utilization = utilization + ramOccupied * 0 (importance is zero so ignore)
- THEN: utilization = utilization (one service only so don't divide)
Also the final section TCPService effectively lets you load balance on number of established connections to your server, so you could balance based on the number of RDP connections to port 3389.
Haproxy Document
For this setting MaxConnections is important to specify as otherwise the agent will have no idea how to calculate the load i.e.
- utilization = MaxConnections / 100 * number of current connections * importance%
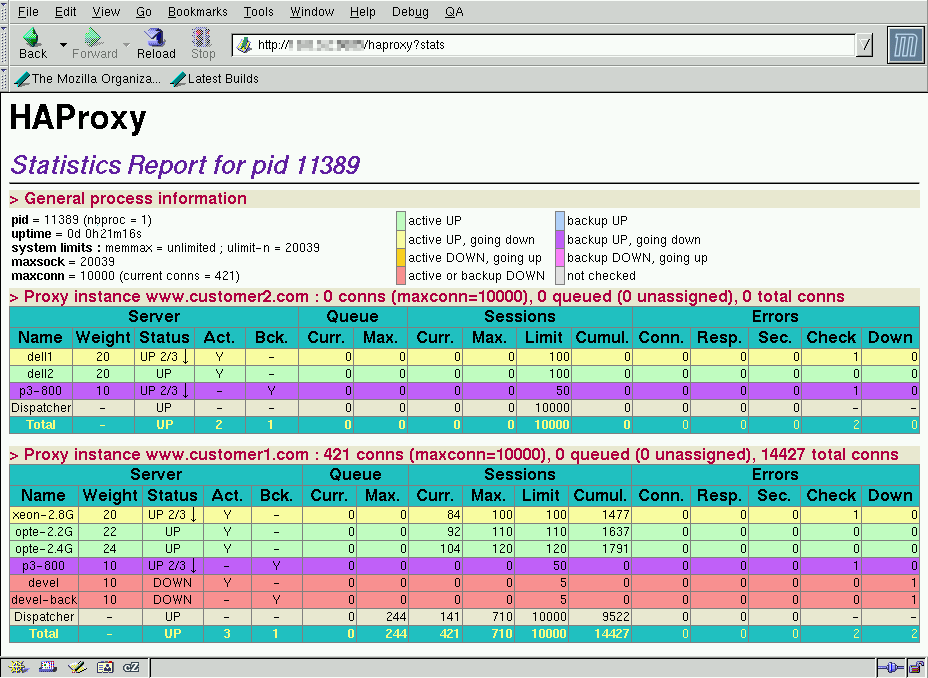
In the following screen shot from a Loadbalancer.org appliance you can see that the Win2008R2 server is healthy and 99% idle, whereas the Linux server was busy at 43% idle before the Linux agent was put into maintenance mode and the server taken out of the group.
Does that make sense? Have a play with the config file and let us know what you think..
The agent functionality is obviously not just for Windows users:
Lets look at an example of load balancing Microsoft RDS with HAProxy:
The important bit agent-check agent-port 3333 tells HAProxy to constantly monitor each backend server in the cluster by doing a telnet to port 3333 and grabbing the response which will usually be a percentage idle value i.e.
- 80% - I am not very busy please increase my weight and send me more traffic
- 10% - I'm busy please decrease my weight and stop sending me so much traffic
- drain - Set the weight to 0 and gradually drain the traffic from this server for maintenance
- stop - Stop all traffic immediately, kill this backend server
- up ready 20% - Force HAProxy to bring the server up and set weight to 20% (irrespective of how it was taken down)
If you have a Linux backend you could create a simple service calling the following script:
Place the script into /usr/bin and call it
Make sure that you make the script executable
Insert this line into /etc/services
Now create the following file called /etc/xinetd.d/lb-feedback
Then change permissions and restart xinetd:
You can now test this service by using telnet:
| It's not Open Source, but it shares its spirit: Why is it important to measure the internal maximum bandwidth of your machine ? Which 10GbE NICs do we recommend ? How can 10GbE load balancing performance be measured ? How to build a 10GbE load balancer with BalanceNG |

Apache: mod_athena
http://code.google.com/p/ath/
Full featured application load balancer for reverse proxy apache httpd mod_proxy.
Apache: mod_proxy_balancer
http://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.1/mod/mod_proxy_balancer.html
mod_proxy and related modules implement a proxy/gateway for Apache HTTP Server, supporting a number of popular protocols as well as several different load balancing algorithms. Third-party modules can add support for additional protocols and load balancing algorithms.
Balance
https://balance.inlab.net
Balanceis Inlab Network's well known open source load balancing solution being a simple but powerful generic tcp proxy with round robin load balancing and failover mechanisms. Its behaviour can be controlled at runtime using a simple command line syntax.
Core Balance
http://core-balance.sourceforge.net/
Core Balance is a TCP Load Balancing proxy. It's goal, unlike many load balancing proxies, is to balance based upon the node speed and available processing cores.
Crossroads
http://crossroads.e-tunity.com/
Looks like being discontinued.
Distributor
http://distributor.sourceforge.net/
Distributor is a software TCP load balancer. Like other load balancers, it accepts connections and distributes them to an array of back end servers. Distributor is compatible with any standard TCP protocol (HTTP, LDAP, IMAP, etc.) and is also IPv6 compatible. Distributor has many unique and advanced features and a high-performance architecture.
Eddie (written in Erlang)
http://eddie.sourceforge.net/

- If CPU importance = 0 then ignore, 0.5 means give 50% importance, 1 means 100% importance
- If RAM importance = 0 then ignore etc.
If ThresholdValue is reached on any monitor then immediately go into DRAIN mode (a value of 0 means no threshold is set).
This can be very useful if you have a small number of RDP sessions using a lot of RAM, simply set a ThresholdValue of 85, then as soon as memory crosses that threshold no new users will be sent to that server.
Otherwise to calculate the percentage idle reported by the agent would be to divide the utilization by the number of factors involved i.e.
If you are using two services then:
- utilization = utilization + cpuLoad * cpuImportance%;
- utilization = utilization + ramOccupied * ramImportance%;
- utilization = utilization / 2
So if importance was 1 for both cpu and ram you would only get 0% reported if both CPU and RAM were 100%. (actually it gets a bit weird if one is already reporting 0%, but lets not worry about that..
And if the importance is zero then ignore completely i.e.
- AS: utilization = utilization + cpuLoad * cpuImportance%;
- IF: utilization = utilization + ramOccupied * 0 (importance is zero so ignore)
- THEN: utilization = utilization (one service only so don't divide)
Also the final section TCPService effectively lets you load balance on number of established connections to your server, so you could balance based on the number of RDP connections to port 3389.
Haproxy Document
For this setting MaxConnections is important to specify as otherwise the agent will have no idea how to calculate the load i.e.
- utilization = MaxConnections / 100 * number of current connections * importance%
In the following screen shot from a Loadbalancer.org appliance you can see that the Win2008R2 server is healthy and 99% idle, whereas the Linux server was busy at 43% idle before the Linux agent was put into maintenance mode and the server taken out of the group.
Does that make sense? Have a play with the config file and let us know what you think..
The agent functionality is obviously not just for Windows users:
Lets look at an example of load balancing Microsoft RDS with HAProxy:
The important bit agent-check agent-port 3333 tells HAProxy to constantly monitor each backend server in the cluster by doing a telnet to port 3333 and grabbing the response which will usually be a percentage idle value i.e.
- 80% - I am not very busy please increase my weight and send me more traffic
- 10% - I'm busy please decrease my weight and stop sending me so much traffic
- drain - Set the weight to 0 and gradually drain the traffic from this server for maintenance
- stop - Stop all traffic immediately, kill this backend server
- up ready 20% - Force HAProxy to bring the server up and set weight to 20% (irrespective of how it was taken down)
If you have a Linux backend you could create a simple service calling the following script:
Place the script into /usr/bin and call it
Make sure that you make the script executable
Insert this line into /etc/services
Now create the following file called /etc/xinetd.d/lb-feedback
Then change permissions and restart xinetd:
You can now test this service by using telnet:
| It's not Open Source, but it shares its spirit: Why is it important to measure the internal maximum bandwidth of your machine ? Which 10GbE NICs do we recommend ? How can 10GbE load balancing performance be measured ? How to build a 10GbE load balancer with BalanceNG |
Apache: mod_athena
http://code.google.com/p/ath/
Full featured application load balancer for reverse proxy apache httpd mod_proxy.
Apache: mod_proxy_balancer
http://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.1/mod/mod_proxy_balancer.html
mod_proxy and related modules implement a proxy/gateway for Apache HTTP Server, supporting a number of popular protocols as well as several different load balancing algorithms. Third-party modules can add support for additional protocols and load balancing algorithms.
Balance
https://balance.inlab.net
Balanceis Inlab Network's well known open source load balancing solution being a simple but powerful generic tcp proxy with round robin load balancing and failover mechanisms. Its behaviour can be controlled at runtime using a simple command line syntax.
Core Balance
http://core-balance.sourceforge.net/
Core Balance is a TCP Load Balancing proxy. It's goal, unlike many load balancing proxies, is to balance based upon the node speed and available processing cores.
Crossroads
http://crossroads.e-tunity.com/
Looks like being discontinued.
Distributor
http://distributor.sourceforge.net/
Distributor is a software TCP load balancer. Like other load balancers, it accepts connections and distributes them to an array of back end servers. Distributor is compatible with any standard TCP protocol (HTTP, LDAP, IMAP, etc.) and is also IPv6 compatible. Distributor has many unique and advanced features and a high-performance architecture.
Eddie (written in Erlang)
http://eddie.sourceforge.net/
Eddie is a high availability clustering tool. It is an open source, 100% software solution written primarily in the functional programming language Erlang (www.erlang.org) and is available for Solaris, Linux and *BSD.
Enhydra Director
http://forge.ow2.org/projects/director
Director is a collection of open source web-server plugins to provide loadbalancing, clustering and unified connection methods for different web-servers on different platforms. The Enhydra Director supports several popular Web servers and operating systems, including Apache (on Linux/Unix and Windows), Netscape Enterprise Server (on Linux/UNIX and Windows), and Microsoft Internet Information Server (on Windows). Director also supports several applications servers: Tomcat (v5.xx and v5.5x), Jetty and Enhydra Application server.
GLB: GitHub's open source load balancer
https://githubengineering.com/glb-director-open-source-load-balancer/
GLB Director is a Layer 4 load balancer which scales a single IP address across a large number of physical machines while attempting to minimise connection disruption during any change in servers. GLB Director does not replace services like haproxy and nginx, but rather is a layer in front of these services (or any TCP service) that allows them to scale across multiple physical machines without requiring each machine to have unique IP addresses.
HAProxy
http://haproxy.1wt.eu/
HAProxy is a free, very fast and reliable solution offering high availability, load balancing, and proxying for TCP and HTTP-based applications. It is particularly suited for very high traffic web sites and powers quite a number of the world's most visited ones. Over the years it has become the de-facto standard opensource load balancer, is now shipped with most mainstream Linux distributions, and is often deployed by default in cloud platforms. Since it does not advertise itself, we only know it's used when the admins report it 🙂
Linux Network Load Balancing
http://lnlb.sourceforge.net/
Linux Network Load Balancing is an open-source project (kernel module + userland app.) aimed to realize decentered network load balancing clusters between Linux boxes.
Linux Virtual Server (LVS)
http://www.linuxvirtualserver.org
The Linux Virtual Server is a highly scalable and highly available server built on a cluster of real servers, with the load balancer running on the Linux operating system. The architecture of the server cluster is fully transparent to end users, and the users interact as if it were a single high-performance virtual server.
Load Balancer Project
http://www.jmcresearch.com/projects/loadbalancer/
Load Balancer Project is an attempt of write a tool that allows to balance request using clusters of servers. The goal is to archieve high availability, load balancing with a simple configuration for the load balancer, and the network topology.
Neutrino
http://neutrinoslb.io/
Neutrino was build keeping the above requirements in mind. It is build in Scala language using Netty Server. It can do L7 routing using canonical names, url context and rule based. It has highly extensible pipeline architecture so that, new modules can be hooked into the pipeline without much work. Developers can add new switching rules and load balancing options easily. New modules can be added to send the log to API end point or load the configuration file from a DB or API. It is using JVM runtime environment, so developers can use either Java or Scala to add modules.
nginx
http://nginx.org
nginx [engine x] is an HTTP and reverse proxy server, a mail proxy server, and a generic TCP/UDP proxy server, originally written by Igor Sysoev. For a long time, it has been running on many heavily loaded Russian sites including Yandex, Mail.Ru, VK, and Rambler.
Octopus Load Balancer
http://sourceforge.net/projects/octopuslb/
Octopus Load Balancer is an extremely fast TCP load balancer with extensions for HTTP to allow balancing based on URI. Features include: server health checks and load polling, dynamic configuration, and the ability to carbon copy incoming requests.
Windows Download Iso
OpenLoBa
http://openloba.sourceforge.net/
OpenLoba was originally created for the VMware Ultimate Virtual Appliance Challenge , and was started on March 10, 2006.
I have been messing around with different ideas and working on small little projects here and there and wanted to make some sort
of project available to the public and the VMware Challenge was the push that got me started. So basically OpenLoBa is a bunch of open source tools put together to make a nice tcp load balancer solution with a web front end.
Pen
http://siag.nu/pen
This is Pen, a highly scalable, highly available, robust load balancer for tcp and udp based protocols such as dns, http or smtp. It allows several servers to appear as one to the outside and automatically detects servers that are down and distributes clients among the available servers. This gives high availability and scalable performance.
Perlbal (implemented in Perl)
http://danga.com/perlbal/
Perlbal is a Perl-based reverse proxyload balancer and web server.[2] Perlbal is maintained by a group connected to Danga Interactive. The program is in common use by large web sites to distribute the load over a number of servers.
Pound
http://www.apsis.ch/pound/
Haproxy Rpm
The Pound program is a reverse proxy, load balancer and HTTPS front-end for Web server(s). Pound was developed to enable distributing the load among several Web-servers and to allow for a convenient SSL wrapper for those Web servers that do not offer it natively. Pound is distributed under the GPL – no warranty, it's free to use, copy and give away.
Riverdrums Load Balancer
http://sourceforge.net/projects/rlb/
The Riverdrums Load Balancer is a feature-full, fast, event-driven frontend to enable high throughput access to clusters.
varnish
http://www.varnish-cache.org/
Varnish Cache is a web application accelerator also known as a caching HTTP reverse proxy. You install it in front of any server that speaks HTTP and configure it to cache the contents. Varnish Cache is really, really fast. It typically speeds up delivery with a factor of 300 – 1000x, depending on your architecture.
XLB HTTP Load Balancer
http://sourceforge.net/projects/xlb/
XLB is a high performance HTTP load balancer. connection management, caching, ssl, scripting. 300 mbit/sec / 4000 reqs/sec takes 30% cpu on a 2GhZ Xeon. connection pooling to backend servers reduces memory and cpu usage on backends.
Zevenet Load Balancer (former Zen Load Balancer)
http://www.zevenet.com
Looks to be commercial now, we'll check this.
